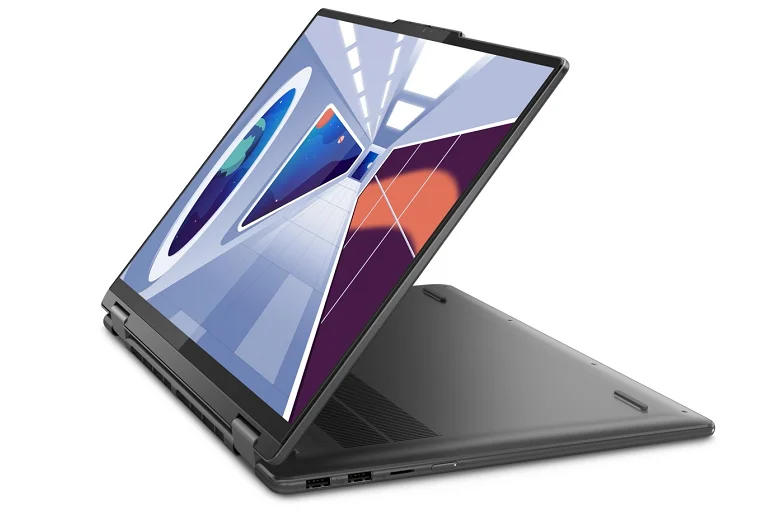
Design
Colour name
Iron Grey
Product type
The sub-category of the product.
Hybrid (2-in-1)
Product colour
The colour e.g. red, blue, green, black, white.
Grey
Form factor
The shape or design of the product.
Convertible (Folder)
Housing material
What the casing of the product is made of.
Aluminium
Display
Touchscreen type
There are a variety of touchscreen technologies that have different methods of sensing touch, including resistive and capacitive.
Capacitive
Display diagonal
Size of the display for this product, measured diagonally, usually in inches.
35.3 cm (13.9″)
Display resolution
The number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It is usually quoted as width × height, with the units in pixels: for example, “1024 × 768” means the width is 1024 pixels and the height is 768 pixels. The higher the number of pixels, the sharper the image.
3840 x 2160 pixels
Touchscreen
A screen of a laptop, smartphone, etc., that responds to touch so you can control the interface using your fingers.
HD type
Type of supported High Definition (e.g. Full HD, 4K Ultra HD).
4K Ultra HD
Touch technology
Technology of touch sensetive screen e.g. dual-touch.
Multi-touch
Panel type
IPS
LED backlight
A backlight is a form of illumination used in liquid crystal displays (LCDs). One type of backlight is made by LEDs, which can be either white or RGB (red green blue). White LEDs are used most often in notebooks and desktop screens, and in virtually all mobile LCD screens. RGB LEDs for backlighting are found in high-end color proofing displays such as HP DreamColor LP2480zx monitor or selected HP EliteBook notebooks, as well as newer consumer grade displays such as Dell’s Studio series laptops which have an optional RGB LED display.
Native aspect ratio
The aspect ratio is the ratio of the width of an image to its height. The native aspect ratio is the one which the projector/display is particularly designed for. Images shown in native aspect ratio will utilize the entire resolution of the display and achieve maximum brightness. Images shown in other than native aspect ratio will always have less resolution and less brightness than images shown in native aspect ratio.
16:9
Display brightness
Brightness is the amount of radiating light emitted from the screen. The brightness rating is measured in candellas per square meter, commonly known as ‘nits’.
300 cd/m²
Dual-screen
Processor
Processor manufacturer
The manufacturer that produced the processor.
Intel
Processor family
A family of processors is a group of processors produced by one company over a short period of time e.g. Intel Pentium processors.
Intel® Core™ i7
Processor generation
8th gen Intel® Core™ i7
Processor model
The model number for the processor in a computer.
i7-8550U
Processor cores
The number of central processing units (‘cores’) in a processor. Some processors have 1 core, others have 2 (e.g. Intel Core Duo) or more (e.g. the Intel Xeon E7-2850 has 10 cores).
4
Processor threads
8
Processor boost frequency
The turbo boost is an automatic, managed accelleration of the processor when one of the cores is overloaded.
4 GHz
Processor frequency
The speed that the microprocessor executes each instruction or each vibration of the clock. The CPU requires a fixed number of clock ticks, or cycles, to execute each instruction. The faster the clocks rate, the faster the CPU, or the faster it can execute instructions. Clock Speeds are usually determined in MHz, 1 MHz representing 1 million cycles per second, or in GHz, 1 GHz representing 1 thousand million cycles per second. The higher the CPU speed, the better a computer will perform.
1.8 GHz
System bus rate
A bus is a communication system that transfers data between components inside a computer, or between computers. The system bus rate is the speed at which data is transferred in this communication system.
4 GT/s
Processor cache
8 MB
Processor socket
Mechanical component(s) that provides mechanical and electrical connections between a microprocessor and a printed circuit board (PCB). This allows the processor to be replaced without soldering.
BGA 1356
Processor lithography
The process which is performed by the processor e.g. CPU (Central Processing Unit).
14 nm
Processor operating modes
Operating modes for the processors that place restrictions on the type and scope of operations for certain processes run by the CPU. This design allows the operating system to run with more privileges than application software.
64-bit
Processor codename
Kaby Lake R
Bus type
OPI
Stepping
Y0
Thermal Design Power (TDP)
15 W
Configurable TDP-up frequency
2 GHz
Configurable TDP-up
25 W
Configurable TDP-down
10 W
Configurable TDP-down frequency
0.8 GHz
Tjunction
100 °C
Maximum number of PCI Express lanes
12
PCI Express slots version
3.0
PCI Express configurations
1×2+2×1, 1×4, 2×2, 4×1
ECC supported by processor
Memory
Internal memory
A computer’s memory which is directly accessible to the CPU.
16 GB
Internal memory type
The type of internal memory such as RAM, GDDR5.
DDR4-SDRAM
Memory clock speed
The frequency at which the memory (e.g. RAM) runs.
2400 MHz
Memory form factor
Design of the memory e.g. 240-pin DIMM, SO-DIMM.
On-board
Maximum internal memory
The maximum internal memory which is available in the product.
16 GB
Storage
Total storage capacity
The total amount of data that can be stored on the device.
1 TB
Storage media
Used for the storage of data e.g. HDD (hard disk drive), SSD (solid-state drive).
SSD
Total SSDs capacity
1 TB
Number of SSDs installed
1
SSD capacity
The Solid State Drive’s data storage capacity.
1 TB
Optical drive type
An optical drive uses laser to read optical discs such as CDs, DVDs and Blu-Ray. Some types of optical drive are: CD ROM drive, CR-RW (CD writer) drive, DVD-ROM.
Card reader integrated
A card reader is a device that enables reading and, in some cases, writing data to and from a memory card.
Graphics
Discrete graphics card model
A graphics adapter (often known as a video card) generates images for a display. A discrete graphics adapter plugs into the motherboard, and usually produces much better graphics than an integrated graphics adapter. There are various models of discrete graphics adapters.
Not available
On-board graphics card
Graphics hardware which is built into the motherboard or CPU, as opposed to a separate graphics adapter (video card). On-board graphics uses CPU and RAM for graphics processing.
On-board GPU manufacturer
Intel
Discrete graphics card
On-board graphics card family
Intel® UHD Graphics
On-board graphics card model
“Graphic adapter” is the hardware that produces images on a display. “On-board” means that the graphics adapter is intergrated inside the motherboard.
Intel® UHD Graphics 620
On-board graphics card base frequency
300 MHz
On-board graphics card dynamic frequency (max)
1150 MHz
Maximum on-board graphics card memory
32 GB
On-board graphics card DirectX version
12.0
On-board graphics card OpenGL version
4.4
On-board graphics card ID
0x5917
Audio
Number of built-in speakers
4
Speaker power
2 W
Built-in microphone
Microphone that is found inside the product.
Number of microphones
2
Camera
Front camera
Camera at the front of the product.
Front camera resolution (numeric)
1 MP
Front camera signal format
720p
Front camera HD type
HD
Network
Wi-Fi
Popular technology that allows an electronic device to exchange data or connect to the internet wirelessly using radio waves.
Top Wi-Fi standard
Connection of this device is done via Wi-Fi in a high standard.
Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac)
Wi-Fi standards
The type of wireless local area network (LAN). It can be ad-hoc, where units in a network communicate peer-to-peer, or Infrastructure, where units communicate with each other via an access point A LAN interconnects computers in a small area e.g. home, school or office.
802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n), Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac)
Mobile network connection
Related products
-

Dell Vostro 3520 Laptop 12th Gen 1255U 15.6inch FHD 512GB SSD 8GB RAM Graphics Windows 11 3520-VOS-1608-BLK
Read more -
HP 250 G10 Intel® Core™ i5 i5-1334U Laptop 39.6 cm (15.6″) Full HD 16 GB DDR4-SDRAM 256 GB SSD Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) Windows 11 Pro Silver
Read more -

HP ProBook G10 Intel® Core™ i5 i5-1334U Laptop 39.6 cm (15.6″) Full HD 8 GB DDR4-SDRAM 256 GB SSD Wi-Fi 6E (802.11ax) Windows 11 Pro Silver
Read more -

HP EliteBook 840 G11 Intel Core Ultra 5 125U Laptop 35.6 cm (14″) WUXGA 16 GB DDR5-SDRAM 512 GB SSD Wi-Fi 6E (802.11ax) Windows 11 Pro AI PC Silver
Read more
